
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus among Korean Children, Adolescents, and Adults Younger than 30 Years: Changes from 2002 to 2016
- Yong Hee Hong, In-Hyuk Chung, Kyungdo Han, Sochung Chung, on Behalf of the Taskforce Team of the Obesity Fact Sheet of the Korean Society for the Study of Obesity
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):297-306. Published online October 26, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0038
- 9,372 View
- 346 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
Despite the importance of and social concern regarding prevention of diabetes at younger ages, limited data are available. This study sought to analyze changes in the prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in Koreans younger than 30 years according to sex, age, and level of income.
Methods
The dataset analyzed in this study was derived from health insurance claims recorded in the National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) database. Participants’ level of income was categorized as low (quintile 1, <20% of insurance premium) or others (quintile 2–5).
Results
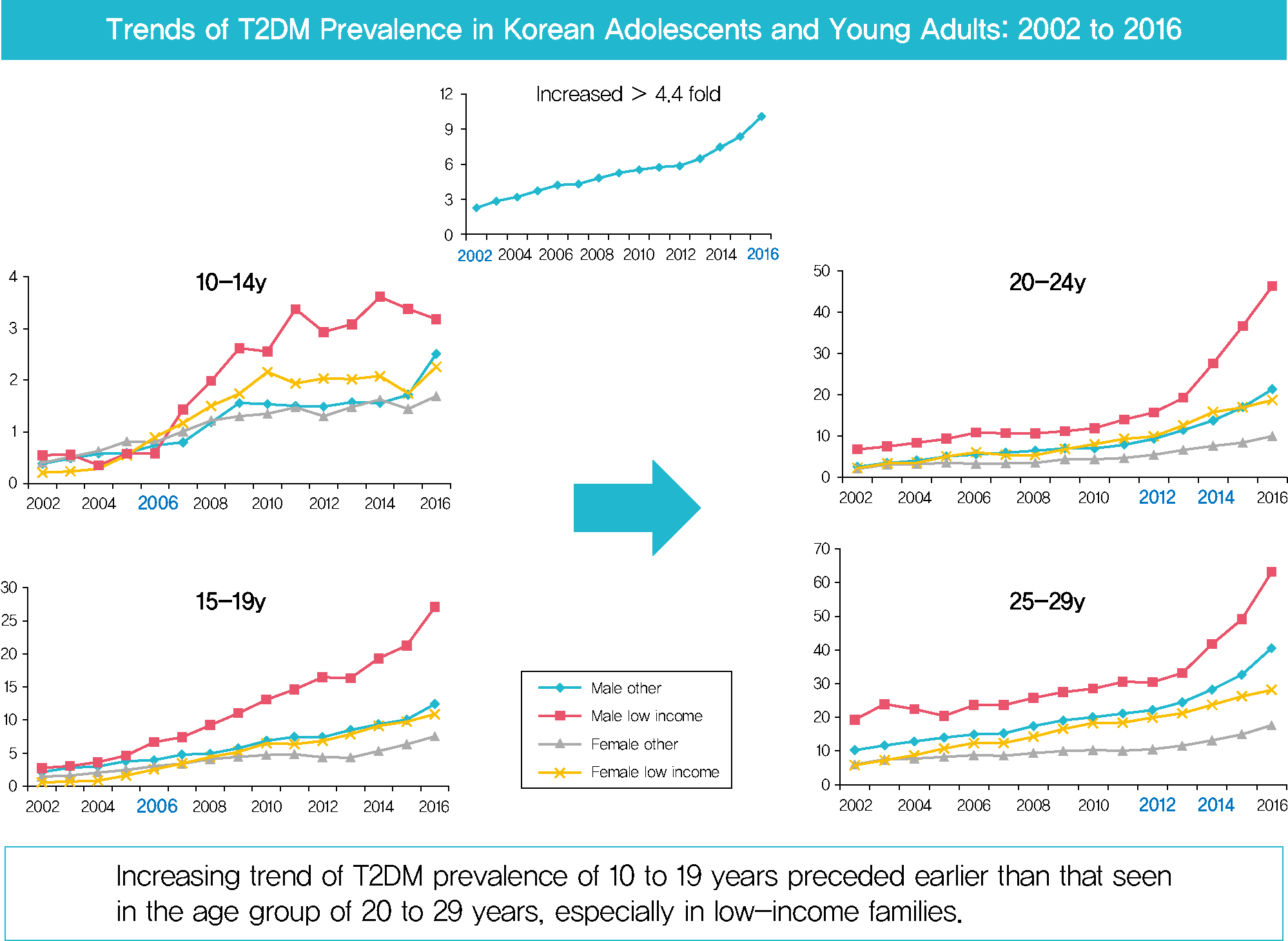
In males and females, the prevalence of T2DM per 10,000 people steadily increased from 2.57 in 2002 to 11.41 in 2016, and from 1.96 in 2002 to 8.63 in 2016. The prevalence of T2DM in girls was higher in the age group of 5 to 14 years. Even though the prevalence was higher among those older than 20 years, the increase had started earlier, in the early 2000s, in younger age group. Adolescents aged 10 to 19 years in low-income families showed a remarkable increase in prevalence of T2DM, especially in boys.
Conclusion
The prevalence of T2DM in young Koreans increased more than 4.4-fold from 2002 to 2016, and the increase started in the early 2000s in younger age groups and in low-income families. This is the first study to examine the trend in prevalence of T2DM in children, adolescents, and young adults in Korea. Future studies and collaborations with social support systems to prevent T2DM at an early age group should be performed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- SCORE and SCORE2 in East Asian Population
JungMin Choi, Soseul Sung, Sue K. Park, Seyong Park, Hyoyeong Kim, Myeong-Chan Cho, Bryan Williams, Hae-Young Lee
JACC: Asia.2024; 4(4): 265. CrossRef - Chronic disease management program applied to type 2 diabetes patients and prevention of diabetic complications: a retrospective cohort study using nationwide data
Min Kyung Hyun, Jang Won Lee, Seung-Hyun Ko
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and pathological characteristics of DKD patients with early-onset type 2 diabetes
Liang Wu, Yi-Yang Zhao, Meng-Rui Li, Dong-Yuan Chang, Ming-Hui Zhao, Min Chen
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2023; 37(8): 108520. CrossRef - Type 2 Diabetes and Its Association With Psychiatric Disorders in Young Adults in South Korea
Min-Kyung Lee, Su-Young Lee, Seo-Young Sohn, Jiyeon Ahn, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Hyuk Lee
JAMA Network Open.2023; 6(6): e2319132. CrossRef - Glycemic control and complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents during the COVID-19 outbreak
Kyeong Eun Oh, Yu Jin Kim, Ye Rim Oh, Eungu Kang, Hyo-Kyoung Nam, Young-Jun Rhie, Kee-Hyoung Lee
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 28(4): 275. CrossRef - Position Statement on the Appropriateness and Significance of Adding the Glycated Hemoglobin Test to the National Health Examination
Ji Hye Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Jaehyun Kim, Sangjoon Park, Kyunghoon Lee, Jun Goo Kang, Eu Jeong Ku, Su Kyoung Kwon, Won Jun Kim, Young Sang Lyu, Jang Won Son, Young Sil Eom, Kyung Ae Lee, Jeongrim Lee, Jung Min Lee, Jung Hwa Lee, Jung Hwa Jung, Hochan Cho, Da
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(4): 178. CrossRef - Trends and Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Adolescents, 2007 to 2018 (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:880-9)
Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 349. CrossRef - Prevalence trends of type 1 and type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents in North Rhine-Westphalia, the most populous federal state in Germany, 2002-2020
C. Baechle, A. Stahl-Pehe, N. Prinz, T. Meissner, C. Kamrath, R.W. Holl, J. Rosenbauer
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 190: 109995. CrossRef - Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Youth
Hwa Young Kim, Jae Hyun Kim
The Ewha Medical Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Affecting High-Risk for Diabetes among Korean Adolescents: An Analysis Using the Eighth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2020)
Kyung-Sook Bang, Sang-Youn Jang, Ji-Hye Choe
Children.2022; 9(8): 1249. CrossRef - Characteristics of Glycemic Control and Long-Term Complications in Patients with Young-Onset Type 2 Diabetes
Han-sang Baek, Ji-Yeon Park, Jin Yu, Joonyub Lee, Yeoree Yang, Jeonghoon Ha, Seung Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, Dong-Jun Lim, Hun-Sung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(4): 641. CrossRef - 젊은 2형 당뇨병 환자의 관리
재현 배
Public Health Weekly Report.2022; 15(35): 2474. CrossRef
- SCORE and SCORE2 in East Asian Population
- Clinical Care/Education
- Frequency of Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose during the School Day Is Associated with the Optimal Glycemic Control among Korean Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes
- Eun Young Joo, Ji-Eun Lee, Hee Sook Kang, Shin Goo Park, Yong Hee Hong, Young-Lim Shin, Min Sohn
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(6):480-487. Published online June 29, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0018
- 4,339 View
- 65 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background This study aimed to evaluate the relationship between the frequency of self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) and glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels among Korean adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). Factors affecting the SMBG frequency were analyzed in order to improve their glycemic control.
Methods Sixty-one adolescents aged 13 to 18 years with T1DM were included from one tertiary center. Clinical and biochemical variables were recorded. Factors associated with SMBG frequency were assessed using structured self-reported questionnaires.
Results Average total daily SMBG frequency was 3.8±2.1 and frequency during the school day was 1.3±1.2. The mean HbA1c level was 8.6%±1.4%. As the daily SMBG frequency increased, HbA1c levels declined (
P =0.001). The adjusted odds of achieving the target HbA1c in participants who performed daily SMBG ≥5 significantly increased 9.87 folds (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.58 to 61.70) compared with those performed SMBG four times a day. In the subjects whose SMBG frequency <1/day during the school day, an 80% reduction in the adjusted odds ratio 0.2 (95% CI, 0.05 to 0.86) showed compared to the group with performing two SMBG measurements in the school setting. The number of SMBG testing performed at school was significantly high for individuals assisted by their friends (P =0.031) and for those who did SMBG in the classrooms (P =0.039).Conclusion Higher SMBG frequency was significantly associated with lower HbA1c in Korean adolescents with T1DM. It would be necessary to establish the school environments that can facilitate adequate glycemic control, including frequent SMBG.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Problems of blood glucose self-monitoring in patients with diabetes mellitus
Yu. A. Kononova, V. B. Bregovskiy, A. Yu. Babenko
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2022; (21-1): 140. CrossRef - Adherence as a Predictor of Glycemic Control Among Adolescents With Type 1 Diabetes: A Retrospective Study Using Real-world Evidence
Sohayla A. Ibrahim, Maguy Saffouh El Hajj, Yaw B. Owusu, Maryam Al-Khaja, Amel Khalifa, Dalia Ahmed, Ahmed Awaisu
Clinical Therapeutics.2022; 44(10): 1380. CrossRef - Self-Care IoT Platform for Diabetic Mellitus
Jai-Chang Park, Seongbeom Kim, Je-Hoon Lee
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(5): 2006. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Adherence to Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose Among Young People with Type 1 Diabetes in China: A Cross-Sectional Study
Wencong Lv, Jiaxin Luo, Qing Long, Jundi Yang, Xin Wang, Jia Guo
Patient Preference and Adherence.2021; Volume 15: 2809. CrossRef - Habits and Routines during Transitions among Emerging Adults with Type 1 Diabetes
Kathleen M. Hanna, Jed R. Hansen
Western Journal of Nursing Research.2020; 42(6): 446. CrossRef - How was the Diabetes Metabolism Journal added to MEDLINE?
Hye Jin Yoo
Science Editing.2020; 7(2): 201. CrossRef - Differences of FreeStyle Libre Flash Glucose Monitoring System and Finger Pricks on Clinical Characteristics and Glucose Monitoring Satisfactions in Type 1 Diabetes Using Insulin Pump
Ayman A Al Hayek, Asirvatham A Robert, Mohamed A Al Dawish
Clinical Medicine Insights: Endocrinology and Diabetes.2019; 12: 117955141986110. CrossRef
- Problems of blood glucose self-monitoring in patients with diabetes mellitus

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





